LiDAR scanning Melbourne
Melbourne has long been recognised as one of Australia’s most advanced engineering and manufacturing centres, and inner-city hubs such as South Yarra sit at the intersection of design, industry, infrastructure, and innovation. As projects become more complex and timelines more compressed, engineering teams are increasingly seeking partners who can reduce uncertainty, improve accuracy, and provide reliable technical insight from day one.
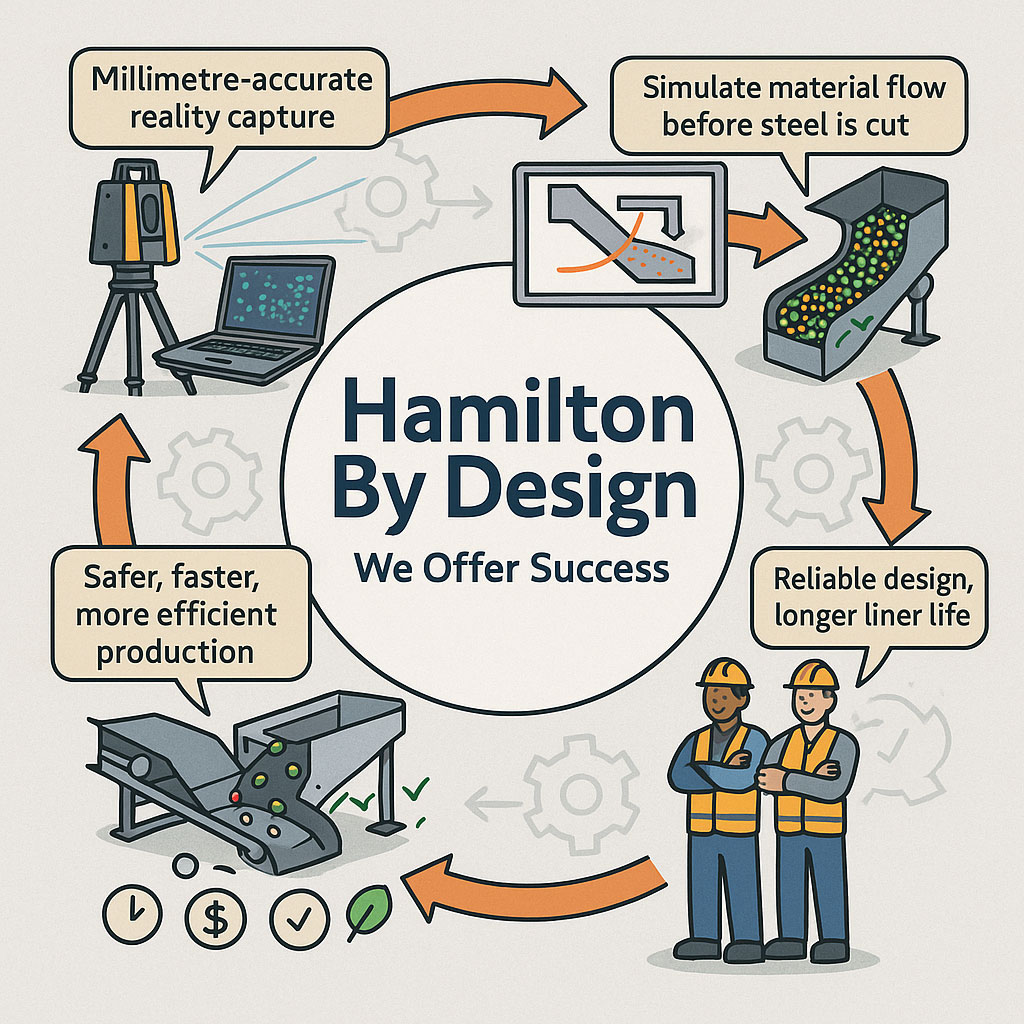
This is where Hamilton By Design delivers genuine value.
Hamilton By Design operates as an engineer-led consultancy focused on precision, constructability, and real-world outcomes. Rather than working from assumptions or incomplete information, the business is built around capturing existing conditions accurately and transforming that data into practical engineering deliverables that support confident decision-making.
Moving Beyond Assumptions in Modern Engineering
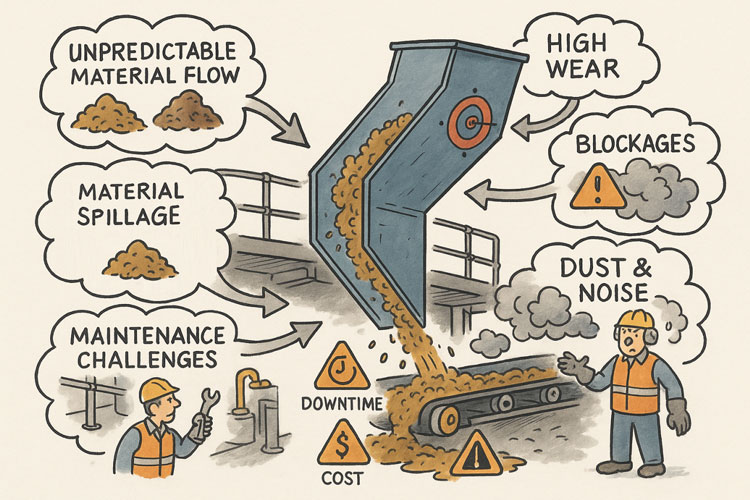
Many engineering challenges in metropolitan Melbourne are not greenfield projects. They involve existing buildings, operating facilities, constrained spaces, legacy assets, or staged upgrades that must integrate seamlessly with what is already in place. In these environments, relying on outdated drawings or manual measurements introduces risk — misalignment, clashes, rework, and delays that can quickly erode budgets and schedules.
Hamilton By Design addresses this challenge by placing reality capture and engineering validation at the front end of projects. This ensures that every downstream decision is based on what truly exists on site, not what is assumed to exist.
For engineering teams working in and around South Yarra — whether supporting manufacturing, infrastructure, plant upgrades, or specialist facilities — this approach significantly reduces technical risk and increases confidence across all stakeholders.
LiDAR Scanning as a Foundation for Accuracy
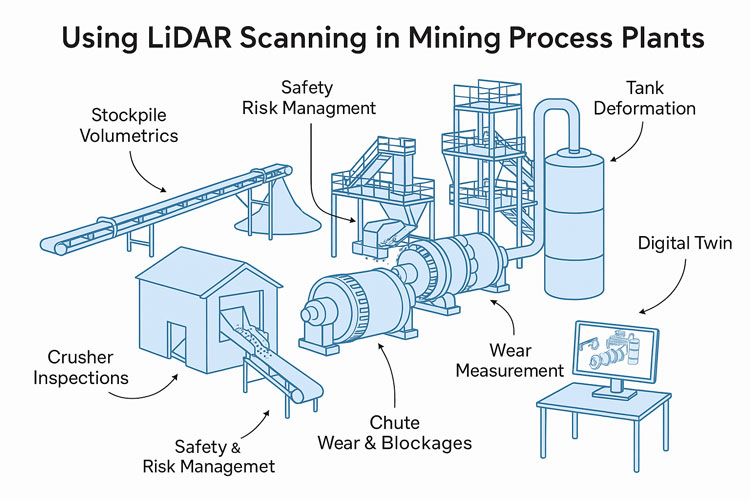
A key capability that differentiates Hamilton By Design is its use of engineering-grade LiDAR scanning. Unlike traditional surveys that capture selective points, LiDAR scanning records millions of measurements across an entire environment, producing a high-resolution digital representation of buildings, plant, structures, and surrounding context.
This data becomes a reliable reference point for engineers, designers, fabricators, and project managers alike.
LiDAR scanning enables:
- Accurate capture of complex geometries and tight spaces
- Clear identification of spatial constraints and interfaces
- Early detection of clashes and access issues
- Reduced need for repeat site visits
- Improved coordination between disciplines
By converting physical assets into precise digital data, Hamilton By Design helps teams eliminate ambiguity and work from a single source of truth.
From Scan Data to Engineering Outcomes
Importantly, Hamilton By Design does not operate as a scanning-only service. The real value lies in how scan data is interpreted, validated, and converted into engineering outputs that directly support delivery.
Scan information is used to develop structured models, layouts, and documentation that reflect real-world conditions. This supports engineering activities such as:
- Mechanical and structural modifications
- Plant upgrades and equipment integration
- Space planning and layout optimisation
- Fabrication and installation planning
- Asset documentation and as-built records
Because the work is led by experienced engineers, the focus is always on what needs to be built, installed, or modified, not just on creating visually impressive models.
Supporting Engineering Teams and Decision-Makers
In a business and engineering environment like South Yarra — where projects are often time-sensitive and commercially driven — external engineering support must be reliable, efficient, and technically sound.
Hamilton By Design integrates smoothly with internal teams, consultants, and contractors, providing additional technical depth without adding unnecessary complexity. The consultancy model is deliberately structured to support decision-makers who need clarity, not noise.
This means:
- Clear communication of constraints and risks
- Practical recommendations grounded in real site data
- Deliverables aligned with fabrication and construction needs
- Engineering documentation that supports approval and execution
The result is fewer surprises downstream and a smoother path from concept through to implementation.
Engineering for Brownfield and Live Environments
One of the most challenging aspects of modern engineering is working within live or brownfield environments — facilities that cannot simply shut down for measurement, redesign, or rework. In these settings, accuracy and planning are critical.
Hamilton By Design’s LiDAR-driven workflows are particularly well suited to these conditions. Rapid data capture minimises disruption on site, while the detailed digital record allows engineering work to continue remotely with confidence.
This approach supports safer planning, better coordination, and reduced exposure to operational risk — outcomes that are highly valued by engineering leaders and project managers alike.
A Practical, Engineer-Led Philosophy
At its core, Hamilton By Design operates on a simple but powerful principle: engineering should be grounded in reality. By combining high-accuracy site data with deep engineering experience, the consultancy helps organisations make informed decisions, avoid costly mistakes, and deliver projects that work the first time.
For organisations operating in South Yarra and the broader Melbourne region, this means access to an engineering partner who understands both the technical and commercial pressures of modern project delivery.
Engineering Certainty in a Complex World
As engineering projects continue to increase in complexity, the margin for error continues to shrink. Those who invest early in accurate data and sound engineering judgement gain a clear advantage — fewer delays, lower risk, and better outcomes.
Hamilton By Design provides that advantage by bridging the gap between the physical site and the engineering office. Through precise LiDAR scanning, practical engineering insight, and a strong focus on constructability, the consultancy supports confident, efficient, and reliable project delivery across Melbourne’s most demanding environments.
LiDAR scanning Melbourne

Our clients: