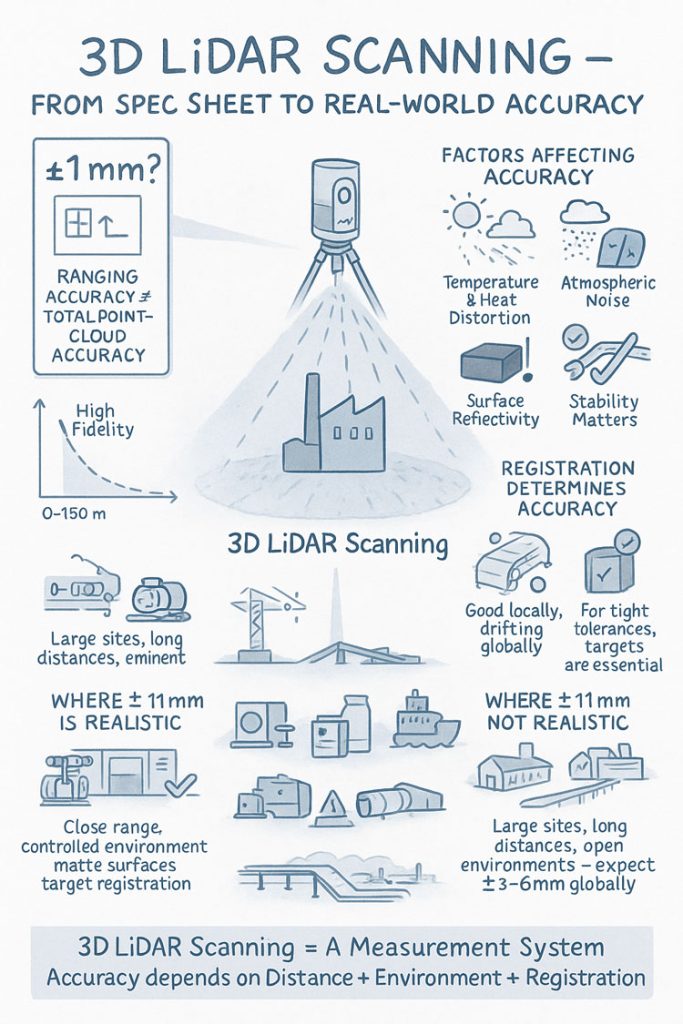
When people first explore 3D LiDAR scanning, one of the most eye-catching numbers in any product brochure is the advertised accuracy. FARO’s Focus S150 and S350 scanners are often promoted as delivering “±1 mm accuracy,” which sounds definitive and easy to rely on for engineering, mining and fabrication work. But anyone who has spent time working with 3D LiDAR scanning in real industrial environments understands that accuracy isn’t a single number — it is a system of interrelated factors.
This article explains what the ±1 mm specification from FARO really means, how accuracy shifts with distance, and what engineers, project managers and clients need to do to achieve dependable results when applying 3D LiDAR scanning on live sites.
1. What FARO’s “±1 mm Accuracy” Really Means in 3D LiDAR Scanning
The ±1 mm number applies only to the internal distance measurement unit inside the scanner. It reflects how accurately the laser measures a single distance in controlled conditions.
It does not guarantee:
- ±1 mm for every point in a full plant model
- ±1 mm for every dimension extracted for engineering
- ±1 mm global accuracy across large multi-scan datasets
In 3D LiDAR scanning, ranging accuracy is just one ingredient. Real-world accuracy is shaped by distance, reflectivity, scan geometry and how multiple scans are registered together.
2. How Accuracy Changes With Distance in Real Projects
Even though the S150 and S350 list the same ranging accuracy, their 3D LiDAR scanning performance changes as distance increases. This is due to beam divergence, angular error, environment and surface reflectivity.
Typical real-world behaviour:
- 0–10 m: extremely precise, often sub-millimetre
- 10–25 m: excellent for engineering work, only slight noise increase
- 25–50 m: more noticeable noise and increasing angular error
- 50–100 m: atmospheric distortion and reduced overlap become evident
- Near maximum range: still useful for mapping conveyors, yards and structures, but not suitable for tight fabrication tolerances
This distance-based behaviour is one of the most important truths to understand about 3D LiDAR scanning in field conditions.
3. Ranging Accuracy vs Positional Accuracy vs Global Accuracy
Anyone planning a project involving 3D LiDAR scanning must distinguish between:
Ranging Accuracy
The ±1 mm value — only the distance measurement.
3D Positional Accuracy
The true X/Y/Z location of a point relative to the scanner.
Global Point Cloud Accuracy
How accurate the entire dataset is after registration.
Global accuracy is the number engineers depend on, and it is normally around ±3–6 mm for large industrial sites — completely normal for terrestrial 3D LiDAR scanning.
4. What Real Field Testing Reveals About FARO S-Series Accuracy
Independent practitioners across mining, infrastructure, CHPPs, plants and structural environments report similar results when validating 3D LiDAR scanning against survey control:
- ±2–3 mm accuracy in compact plant rooms
- ±5–10 mm across large facilities
- Greater drift across long, open, feature-poor areas
These outcomes are not equipment faults — they are the natural result of how 3D LiDAR scanning behaves in open, uncontrolled outdoor environments.
5. Why Registration Matters More Than the Scanner Model
Most real-world error in 3D LiDAR scanning comes from registration, not the laser itself.
Cloud-to-Cloud Registration
Good for dense areas, less reliable for long straight conveyors, open yards or tanks.
Target-Based Registration
Essential for high-precision engineering work.
Allows tie-in to survey control and dramatically improves global accuracy.
If your project needs ±2–3 mm globally, target control is mandatory in all 3D LiDAR scanning workflows.
6. Surface Reflectivity and Environmental Effects
Reflectivity dramatically affects measurement quality during 3D LiDAR scanning:
- Matte steel and concrete return excellent data
- Rusted surfaces return good data
- Dark rubber, black plastics and wet surfaces reduce accuracy
- Stainless steel and glass behave unpredictably
Environmental factors — wind, heat shimmer, dust, rain — also reduce accuracy. Early morning or late afternoon typically produce better 3D LiDAR scanning results on mining and industrial sites.
7. When ±1 mm Is Actually Achievable
True ±1 mm accuracy in 3D LiDAR scanning is realistic when:
- Working within 10–15 m
- Surfaces are matte and reflective
- Registration uses targets
- Tripod stability is high
- Conditions are controlled
This makes it suitable for:
- Pump rooms
- Valve skids
- Structural baseplates
- Reverse engineering
- Small mechanical upgrades
But achieving ±1 mm across a full plant, CHPP, or yard is outside the capability of any terrestrial 3D LiDAR scanning workflow.
8. S150 vs S350: Which One for Your Accuracy Needs?
S150 – Engineering-Focused Precision
Ideal for industrial rooms, skids, structural steel and retrofit design work where short-to-mid-range accuracy is essential.
S350 – Large-Area Coverage
Perfect for conveyors, rail lines, yards, and outdoor infrastructure.
Global accuracy must be survey-controlled for tight tolerances.
Both scanners deliver excellent 3D LiDAR scanning performance, but the S150 is the engineering favourite while the S350 is the large-site specialist.
9. What to Specify in Contracts to Avoid Misunderstandings
Instead of stating:
“Scanner accuracy ±1 mm.”
Specify:
- Local accuracy requirement (e.g., ±2 mm at 15 m)
- Global accuracy requirement (e.g., ±5 mm total dataset)
- Registration method (mandatory target control)
- Environmental constraints
- Verification method (e.g., independent survey checks)
This ensures everyone understands what 3D LiDAR scanning will realistically deliver.
10. When a Terrestrial Scanner Is Not Enough
Do not rely solely on 3D LiDAR scanning for:
- Machine alignment <1 mm
- Bearing or gearbox placement
- Certified dimensional inspection
- Metrology-level tolerances
In these cases, supplement scanning with:
- Laser trackers
- Total stations
- Metrology arms
- Hybrid workflows
Conclusion: The Real Truth About 3D LiDAR Scanning Accuracy
FARO’s S150 and S350 are outstanding tools for industrial 3D LiDAR scanning, but the ±1 mm spec does not tell the full story. Real-world accuracy is a combination of:
- Distance
- Registration method
- Surface reflectivity
- Site conditions
- Workflow discipline
When used correctly, these scanners consistently deliver high-quality, engineering-grade point clouds suitable for clash detection, retrofit design, fabrication planning and as-built documentation.
3D LiDAR scanning is not just a laser — it is an entire measurement system.
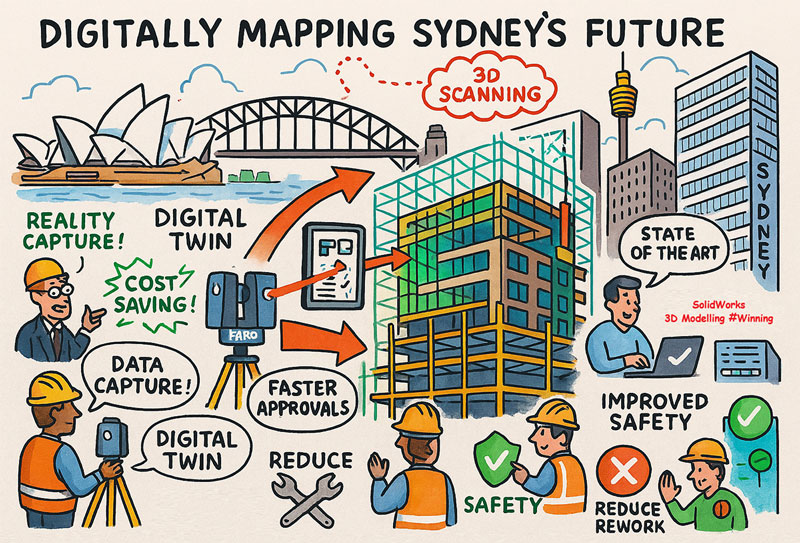
And when the system is applied with care, it produces reliable, repeatable data that reduces rework, improves safety, and strengthens decision-making across mining, construction, fabrication and industrial operations.
Where Is your project

3D CAD Modelling | 3D Scanning