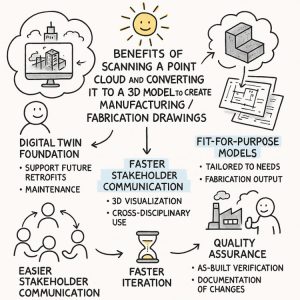
3D Laser scanning is the art form of a controlling a visible deflection of laser beam that captures a set of points from a specific datum to derive a virtual reflection of a known space or envelope.
This space or envelope is recorded as a data set of existing geometry. This existing geometry can be converted or imported in a 3-D solid modelling environment where 3-d Solid models can be created in either a top down or bottom modelling environment.
Just as one needs to focus a camera to generate a crisp image point cloud scanning has the same need to focus on the subject along with the datum.
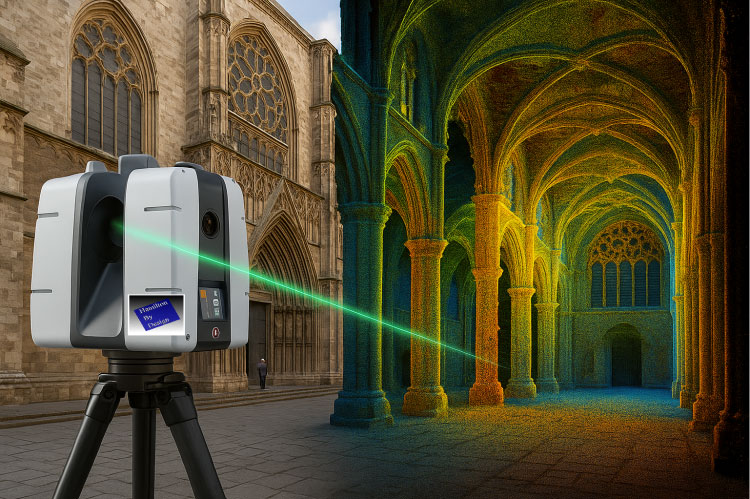

What Differentiates 3D LiDAR Scanning for Mechanical Engineering Projects?
In mechanical engineering and industrial environments, accurate site data is critical for effective design, maintenance, and upgrades. 3D LiDAR scanning offers a superior method of data collection when compared to both traditional manual measurements and existing as-built drawings.
Compared to As-Built Drawings
As-built drawings are traditionally relied on to understand existing site conditions. However:
-
They’re often outdated — plants evolve over time, and many changes (especially minor ones) are undocumented.
-
Prone to inaccuracy — hand-markups and field changes rarely reflect actual conditions.
-
2D limitations — As-builts typically lack depth or 3D spatial relationships critical in retrofit or modification work.
LiDAR scanning, by contrast, captures a real-time 3D snapshot of the current environment, producing a true digital twin of the site — not just what was designed, but what actually exists.
Compared to Manual Measurement
While traditional measuring tools (tape, laser distance meters, total stations) are useful, they:
-
Are time-consuming, particularly on complex or congested sites
-
Require access to all measurement points, which may be difficult or hazardous
-
Capture limited data, often needing interpretation or manual CAD input
LiDAR scanning collects millions of accurate data points in minutes — safely and efficiently — from a distance.
Key Advantages of 3D LiDAR Scanning
| Feature | 3D LiDAR Scanning | As-Built Drawings | Manual Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Millimetre-level | Varies (often outdated) | Medium (depends on access) |
| Data Currency | Real-time, current site | Often outdated | Current, but limited scope |
| 3D Context | Full 3D spatial capture | 2D or basic 3D | No 3D unless modeled |
| Safety | Remote capture possible | N/A | Requires physical access |
| Time Required | Rapid (minutes to hours) | N/A (pre-existing) | Slow (hours to days) |
| CAD/BIM Integration | Seamless | Manual redrafting required | Manual input required |
Why This Matters in Engineering Projects
-
Design accuracy: Helps avoid costly mistakes and rework.
-
Clash detection: Identify interferences before fabrication or installation.
-
Brownfield integration: Match new designs precisely to existing geometry.
-
Shutdown efficiency: Reduce site visits and prep time with remote planning.
While as-built drawings and manual measurement have their place, 3D LiDAR scanning represents a leap forward in accuracy, efficiency, and safety. For mechanical engineering projects — especially in mining, power, and processing industries — it provides confidence in the data and clarity in the design process

Where is your project ?

Our clients:

Mechanical Engineering | Structural Engineering
Mechanical Drafting | Structural Drafting
3D Laser Scanning | 3D CAD Modelling | 3D Scanning
SolidWorks Contractors in Australia

3d laser scanning for engineering